Melanoma is a type skin cancer that is associated with UV radiation. Its incidence in the united states is rising. It is usually pigmented but it can also be without pigmentation (amelanotic). Most cases of melanoma arise from a pre-existing nevus. Melanoma accounts for majority of death from skin cancer. It is slightly more common in men and about 20% of all melanoma occur in the head and neck area. According to the American cancer Society 2009 data, it accounts for about 5% of cancers diagnosed in men and about 4% of cancers in women.
Risk factors
- Acute intense intermittent sunburns
- Especially at young age
- Immunosuppression
- Hereditary Syndromes (10% of cases)
- Two first-degree relatives or three relatives.
- Risk is 2-8x baseline
- Features: blue/green eyes, blond/red hair, light complexion, freckles
- 2% (1 in 50) for whites, 0.1% (1 in 1,000) for blacks
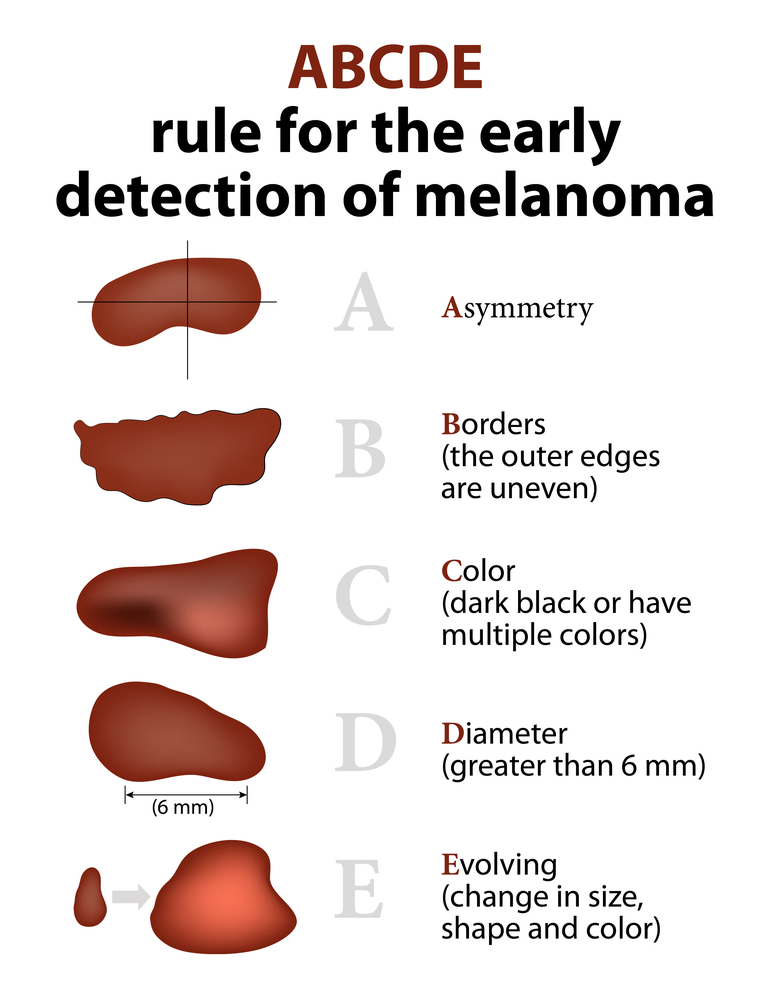
ABCDE of Melanoma
- Asymmetry: Melanoma lesions are often irregular in shape. Benign moles are usually symmetrical.
- Border: Benign moles usually have smooth and even borders. Melanoma lesions usually have irregular borders that are difficult to define.
- Color: Benign moles usually have a single shade of color. The presence of more than one color (blue, black, brown, etc.) or the uneven distribution of color may be a concerning sign.
- Diameter: Melanoma lesions are often greater than 6 millimeters in diameter.
- Evolution: The evolution of a mole is one of the most important factors to consider when it comes to diagnosing melanoma.
Types of Melanoma
Superficial spreading
- Most Common (70%)
- Flat during early phase
- Typically from pre-existing nevus
- 5-7 years of radial growth phase
Nodular
- About 15% of all Melanomas
- Short radial growth phase, early vertical growth
Acral lentiginous
- 2%–8%, Palms, soles, nail beds
- Equal amongst whites/blacks
- Aggressive, early vertical growth
Lentigo maligna
- 10%, Prolonged radial growth -10 years
- Arise from premalignant areas (Hutchinson freckle)
- proclivity for the dermal-epidermal junction and tend to follow hair follicles
- 5% risk of transformation to invasive MM
- Can have unpredictable subclinical extension
Desmoplastic
- Overall rare and may be without pigmentation (Amelanotic 5%)
- Associated with perineural invasion
- Pure desmoplastic melanoma is associated with lower rate of nodal metastasis
Mucosal
- About 2% of all melanoma cases and is associated with poorer prognosis